Needless to add, India has moved towards regulating cryptocurrencies with a firm hand particularly via the parameters governing Crypto Tax India. The tax regime announced in 2022 and bolstered year after year, was created to ensure that profits from speculative cryptocurrency investments were taxed properly. The basic tax on income from the circulation of cryptocurrency 30% flat No matter how small the trade or what crypto asset is traded, this tax applies.
The taxable events under this regime include converting cryptocurrency into INR, exchanging one crypto with another and using it to buy goods or services as well. As these rules do not provide any exemptions or relief, it has raised concerns among investors so far with making Crypto Tax India one of the most aggressive tax policies globally.
Crypto Tax India: Transactions and Taxable Events
The Crypto Tax India framework spares very few cryptocurrency-related activities from being taxable events. Besides taxation at 30% on profits, a Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) of 1 per cent is applicable currently for any cryptocurrency transaction worth over ₹10,000 in a fiscal year. This TDS is valid in fiat-to-crypto transactions as well the crypto trading against this law where buyer and seller both would be liable to make sure that they are abiding by it. The intent behind this TDS is to lead a discrete trail of cryptocurrency investments, the purpose more transparency in space and curb tax evasion.
The 1% TDS is interesting because it deducted on the entire transaction amount and not just gains. With this, however low the amount of loss incurred by a trade would be burnt from TDS. In addition to this, it also states that exchanges operating in India deduct TDS automatically and for peer-to-peer (P2P) or international transactions the responsibility of deducting and depositing the TDS falls on an investor. The rate of application set in the Crypto Tax India framework results in its being more comprehensive and onerous for cryptocurrency investors, particularly those conducting trades internationally.
Crypto Tax India: Investor Challenges and Lack of Relief
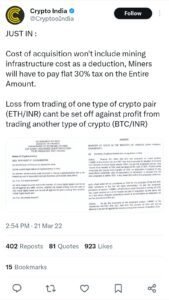
Biggest Criticism: Inflexibility of Crypto Tax India for Investors By contrast with other capital assets, however in the case of crypto losses cannot be offset against gains. So, for example if an investor trades Bitcoin and makes a profit of ₹1 lakh in one financial year but loses ₹80,000 from Ethereum during the same period then they are required to pay 30% tax over his full ₹₹1 lakh- irrespective he has only kept total amount of Rupees twenty thousand as net income. The inability to set off losses from one trade against profits in another makes crypto trading much more expensive.
Moreover, the framework does not have a solution for cryptocurrencies lost to scams or because of forgotten passwords and stolen wallets. This means that if an investor loses their digital assets forever, the lost digital asset is still considered transferred and needed to be taxed. This further complicates the picture as investors are now on the hook for taxes for assets that they no longer own. For years the community has sought changes that would permit deduction of losses and provide explicit guidelines for when catastrophe strikes, yet those calls were disregarded in the 2024 spending plan.
Which makes Crypto Tax India one of the harshest cryptocurrency tax regimes in all over world with very limited scope for error or loss. Be informed and detailed in your records of each trade to adhere to the law as an investor. The sooner this part of crypto market in India matures, the better for all parties involved whether it is long term investors or those who has incurred losses. For the time being, people in India involved with cryptocurrency will need to keep obeying those rules!
Most Related News Here.