Understanding Crypto Custody
Over the past few years, with general acceptance of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum and many others, there has been a concern among individuals and institutional investors about how to safely store these digital assets. Our goal is to answer this question and discuss the importance of crypto custody, a fundamental service that guarantees cryptocurrencies are always safe from digital threats in today’s complicated online climate.
This article will dive into what crypto custody is, the various types available and why it should be a priority for beginners as well as experienced users of cryptos.
What Is Crypto Custody?
At its simplest, cryptocurrency custody is the practice of safely storing and managing digital assets (typically cryptocurrencies) on behalf of others. Cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, are maintained in a blockchain—the decentralized counterpart of traditional bank accounts. A private key (similar to a rumored password) and public key (equivalent of your bank account number), are necessary for accessing and doing anything with the digital assets.

The one thing a user absolutely cannot lose is their private key, as it has the potential to grant anyone who finds or knows the right combination control over all the assets tied to these keys. Because if it is lost, stolen or compromised, then there will be no way of getting the cryptocurrency back, leaving security at highest priority.
What is a Crypto Custody Solution?
A Crypto Custody Solution is a security service provided by third-party companies to safely store significant amounts of cryptocurrency. These are essentially services catered towards large investors, namely: Hedge funds Cryptocurrency exchanges Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) Let’s dissect the situation:
Who uses it?
- Institutional investors holding large amounts of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other digital assets.
Why do they use it?
- To protect their investments from theft, hacking, or loss.
How does it work?
They use two main methods for storage:
- Hot storage (connected to the internet) for quick access but higher risk of being hacked.
- Cold storage (disconnected from the internet) for greater security but less convenient for immediate use.
Key Factors of Crypto Custody:
- Custody means having control or responsibility for protecting something. In this case, it’s about keeping cryptocurrency safe.
- Crypto custody is how cryptocurrency is protected by securely storing the private keys (codes) that allow access to digital wallets.
- There are several types of crypto custody, each with its own pros and cons:
– Hot storage (online) allows fast access but is riskier.
– Cold storage (offline) is more secure but slower to access.
- Crypto custody companies offer secure storage services for investors or institutions with large cryptocurrency holdings, often in the millions or billions.
- The largest crypto custody providers are:
– Coinbase: manages $200 billion+ in assets.
– Gemini: manages around $30 billion.
– BitGo: provides custody for over $64 billion worth of crypto.
- As the cryptocurrency market grows (valued at $1 trillion+ in 2023), the demand for crypto custody solutions will likely increase too.
Types of Crypto Custody
There are two primary forms of crypto custody: self-custody and third-party custody.
1. Self-Custody
Self-custody refers to managing your own private keys without relying on a third party. This means that the individual or institution is solely responsible for the security and management of their digital assets. While self-custody gives the user full control and independence over their cryptocurrencies, it also places the burden of security directly on them.
Methods of self-custody include:
- Hardware Wallets: These are physical devices that store the private keys offline, making them highly resistant to hacking. Examples include Ledger and Trezor.
- Software Wallets: These are applications that store private keys on a device like a computer or smartphone. While more convenient, software wallets are more vulnerable to online threats like malware.
- Paper Wallets: This involves printing out the private keys or seed phrases on paper. Though immune to online attacks, paper wallets can be easily lost, stolen, or damaged.
The primary advantage of self-custody is independence and full control. However, the risk lies in the fact that if a user loses access to their private key, they lose access to their cryptocurrency—forever.
2. Third-Party Custody
Third-party custody, on the other hand, involves entrusting the storage and management of digital assets to a professional custodian, such as a cryptocurrency exchange, a specialized crypto custodian, or even traditional financial institutions that offer crypto services.
These custodians typically provide:
- Secure Storage: Often using multi-layered security protocols such as cold storage (offline storage), encryption, and physical vaults.
- Insurance: Some custodians offer insurance coverage for digital assets in the event of theft or loss due to security breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance: Third-party custodians often comply with regulations, offering more transparency and security assurances for institutional investors.
- Convenience: By outsourcing the responsibility of key management, investors—especially institutions—are free from the technical and logistical challenges of safeguarding their own private keys.
Third-party custody solutions are widely adopted by institutional investors, such as hedge funds, family offices, and corporations that handle large volumes of cryptocurrencies. It provides peace of mind through professional oversight and eliminates the technical complexities associated with self-custody.
3. Partial Custody
Partial custody arrangements split the responsibility of protecting private keys between multiple entities. This method is particularly good for shared accounts (e.g., the same cryptocurrency among a couple).
One of the most well-known is what we call “partial custody.” 1. Multisignature (Multisig) & 2. Technologies for Secure Multiparty Computation (MPC).
Multisignature (multisig)
Multisignature is a security feature where multiple private keys are jointly needed to approve a transaction, rather than just one key. For example, a multisignature wallet might require 2 out of 3 keys or 3 out of 5 keys to be used before the transaction can happen. It avoids any one person having all the power, so that the risk of theft or error is reduced.
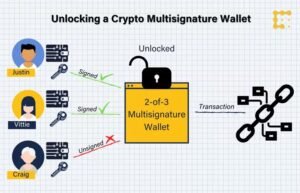
It’s like a bank vault that requires more than one manager to turn their keys at the same time to open it; no one can go alone to the bank vault. And it’s generally used for companies holding large amounts of assets.
Secure Multiparty Computation (MPC)
Multi-party computation (MPC): This is the secret sharing scheme used to split a private key into multiple keys and distribute them among many stakeholders. Each party uses their secret part to confirm a transaction without disclosing its data to others. The system simply combines parts of these to verify the transaction, but no one person sees an entire key.
MPC, working off-chain (thus the private setting of details like number A dedicated groupActive or how many approvers), in contrast to MultiSig. It’s similar to baking a cake, where everyone puts their own ingredient but no one knows what others added, and the only thing revealed is the final cake.
How crypto custody solutions work?
Custody solutions for storing and protecting cryptocurrency work because they manage private keys. Keys, just like passwords, are used to interact with your digital assets. Not the person, but the wallet, where the keys are stored, can be a “custodian.” Wallets can store a single cryptocurrency, e.g., Bitcoin, or multiple assets; sometimes there are hundreds of them.

If we’re talking about a custodian wallet, the keys will be managed by the company. Sometimes, the owner of the assets never possesses those keys. Thus, the account can be restored by the custodian, the equipment for the best protection of keys can be selected, and everything else of that kind is done. If a person forgets his or her password, there is no need to worry, we just have to verify your identity and then everything in the account will be as in the new one. The account can be recovered within 1 to 2 business days.
Those who want to control everything use personal wallets, usually hardware, like Ledger Nano or Trezor wallets. This approach is usually used to store anywhere from one to dozens of different cryptocurrencies in a single wallet. Here, the owner fully manages the keys, but this is very risky because if a person forgets the password or loses his keys, the money will be lost forever, there is no way to recover the account, and this is real. I have read that about 20 percent of all existing bitcoin is lost in this way.
The Importance of Crypto Custody
The need for secure crypto custody has become increasingly apparent as the digital asset market matures. Unlike traditional financial assets held in a bank or brokerage account, cryptocurrencies are bearer instruments—meaning that whoever holds the private keys essentially owns the asset. Without proper security measures, digital assets are vulnerable to a range of risks, including:
- Theft: Cyberattacks targeting exchanges or wallets can lead to significant losses. High-profile cases like the Mt. Gox hack in 2014, where 850,000 bitcoins were stolen, demonstrate the need for secure custody solutions.
- Loss of Private Keys: Whether through human error, hardware failure, or accidents (like losing a paper wallet), losing access to private keys means losing access to the cryptocurrency, often irretrievably.
- Regulatory Compliance: For institutional investors, regulatory frameworks require a level of security and accountability that is only achievable through robust custody services. Custodians help meet these requirements by offering audit trails, insurance, and transparency.
Self-Custody vs. Third-Party Custody: Which Is Right for You?
Choosing between self-custody and third-party custody depends on the individual’s or institution’s level of expertise, the value of the assets being managed, and the level of risk tolerance.
For individual investors who prioritize independence and control, self-custody might be the better option, as long as they are confident in their ability to securely manage their private keys. Self-custody can offer more privacy and lower fees since there is no intermediary.
For institutional investors or those with significant cryptocurrency holdings, third-party custody is often a more practical and secure option. Entrusting assets to a professional custodian offers a higher level of security, compliance with regulations, and added peace of mind, making it ideal for businesses and large-scale investors.
SEC Rule for Crypto Custody
The SEC’s safeguarding rule requires investment advisers to store all assets, including crypto, with a “qualified custodian” (e.g., banks, trust companies).
This rule, from the 1940 Investment Advisers Act, ensures assets are protected from theft or mismanagement. It applies to all assets held for investors, not just crypto.
The Future of Crypto Custody
As the cryptocurrency market continues to grow, so does the demand for reliable and secure custody solutions. The landscape is evolving, with banks and traditional financial institutions increasingly offering crypto custody services alongside established players in the crypto space. Innovations in cryptographic security, such as multi-signature wallets, decentralized custody solutions, and advancements in encryption technology, will continue to shape the future of crypto custody.

Ultimately, crypto custody is an essential service that allows individuals and institutions to safely participate in the digital asset economy. Whether through self-custody or by relying on third-party custodians, securing digital assets is vital in ensuring the long-term success and trust in cryptocurrencies.












